Painful and Swollen Knee with Red Skin—Synovitis
Ask a QuestionHave you ever experienced knee pain or heard complaints about it? Although it only occurs in the knee, the pain may affect your activity, such as walking and lifting the leg. If your knee looks reddish and swollen, it is best to see a doctor as soon as possible as you may have synovitis on the knee. Delayed treatment can lead to chronic diseases and impact your future life.
Overview- What is synovitis?
Synovitis is a disease that mainly occurs in the joint of the knee. It can also affect the joints of the ankle, wrist, elbow, hand, foot and shoulder. There are many synovial membrane coatings in the head of a joint that secrete lubricating fluid to nourish the joint and build a linked bridge between each joint. However, affected by some stimulants (osteoarthritis, arthritis, rheumatism, trauma, bone injury, surgery and so on), the synovial membrane may become infected and secrete a harmful effusion that creates the aching feeling. Doctors diagnose synovitis mainly because of the extra effusion in the test image.
The knee has the largest articular surface and the most complicated joint construction. The synovial membrane of the knee joint is largely transmitted under the soft skin, so the risk of infection and lesion in the knee is higher than in other joints. Sprains and other injuries are the most common causes of synovitis in the knee. (The following picture of synovial joint gives you a better understanding.)
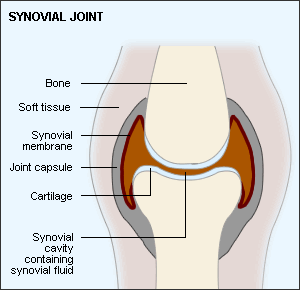
Synovitis can lead to temporary or long-standing disabilities that can affect work or family. Although modern medicine has found effective ways of treating synovitis, most patients do not completely heal. So, instead of finding an optimal way to treat synovitis, protecting your joints and avoiding injury is more advisable to prevent synovitis.
The most common symptoms of synovitis of the knee are as follows:
• Swollen and painful knee
• Bloodshot/reddish skin of the knee
• Difficulty to squat
• Limited walking
• Difficulty bending the knee
*This article mainly talks about ‘synovitis of knee’ (hereinafter referred to as ‘synovitis’).
Cause of synovitis
Synovitis often occurs in three groups: young people, seniors and athletes.
1. Young people
Almost all cases of synovitis in young people are caused by sprains and injuries of the knee. For example, a torn meniscus, ligament injury and effusion in the joint can affect the entire knee. Other minor injuries, such as dislocation, are the result of a lesion in the synovial membrane, mainly in the form of a light wound or chronic knee strain. In addition, according to Chinese medicine, when patients suffer from wind, cold and damp during the onset of synovitis, their knee may swell and become less flexible, resulting in chronic synovitis.
Apart from sprains and injuries, infection is also a trigger of synovitis in young people.
Normally, the blood vessel in the synovial membrane provides the blood circulation with a suitable environment that contributes to the improvement of the defence ability against bacteria. However, if you are attacked by bacteria, such as tubercle bacillus, they can spread at high speed in the bloodstream, attacking the synovial membrane, which copies numerous bacteria and forms a lesion in the knee surface. This progression develops slowly and is difficult to recognise so that it develops into chronic synovitis.
2. Seniors
In the elderly, synovitis often occurs after the onset of osteoarthritis. This is related to cartilage degeneration and bone hyperplasia, the hallmarks of osteoarthritis, which results in the production of more stimulants that induce oedema and effusions in the synovial membrane of the knee.
3. Athletes
Overexertion or improper posture during exercise can result in excessive strain on the knee, causing oedema in the tissue and blood vessel dilatation of the synovial membrane. Under this condition, the blood plasma and cells will leak and fill the membrane in the form of effusion. If the effusion gradually accumulates in the knee, the knee may feel injured and swollen. A recurrent lesion in the knee without any treatment can trigger a chronic inflammation. Therefore, it is essential to perform warm-up exercises and to wear protective equipment, such as kneepads, before doing any sports.
Treatment of synovitis
Patients with synovitis should avoid doing excises that may injure the knee and increase the load on the knee. If the situation is severe, you should lie down on the bed and exercise the quadriceps (muscle above the knee) at home. For instance, lifting the affected leg can increase blood flow and absorb the excess effusion in the joint, helping to remove the swelling and pain. There are other treatments that you can do at home.
1. General treatments
If you feel only mild pain in the knee without any other symptoms of synovitis, there are a few methods you can use:
1) Have a rest. Let your knee take a break, avoid stairs or mountaineering. The continuous activity of the knee may worsen the pain.
2) Use ice packs. Low temperatures can quickly ease the pain. Try to put an ice pack or ice bottle on the affected knee. In case of freezing injuries, it is better to wrap the ice with a washcloth before applying.
3) Wearing a knee pad can protect your knee and support knee activities. Remember to ask your doctor before buying a knee pad.
4) Take painkillers such as ibuprofen and naproxen, which can diminish inflammation and alleviate the pain. After excluding other conditions, such as gastric ulcer and renal dysfunction, you can take the OTC medication as recommended in the package leaflet.
5) Applying medicinal cream is a safe and effective method to treat synovitis. You can find the following three medications in most pharmacies.
• Penetrex Pain Relief Cream
Apply Penetrex anywhere you experience pain. It helps relieve or eliminate inflammation and is suitable for people with knee pain, arthritis, plantar fascia, shoulder pain, sciatica and chronic pain.
• Bengay Ultra Strength Cream
The pain-relieving ingredients of Bengay can relieve mild joint and muscle pain by speeding up blood circulation. You may feel heated an after application. Bengay is suitable for strains, rheumatoid arthritis and muscle or joint pain (in the knee, shoulder and waist.)

• Tiger Balm Pain Relieving Ointment
Tiger Balm, a popular medication in Asia, can not only alleviate muscle pain, but also relieve itching caused by insect bites.

2. Puncture therapy
As the affected knee accumulates more and more effusion, putting considerable pressure on your knee, your doctor will consider puncture therapy. During the therapy, the additional effusion and blood are completely removed, and the doctor will inject the sodium hyaluronate into the joint cavity. Sodium hyaluronate, the main constituent of synovial fluid, covers the surface of articular cartilage, which protects either cartilage or synovial membrane from degrading. Puncture therapy can alleviate knee pain and restore joint activity.
3. Massage Therapy
Wash hands and rub them together until warm. Sit in bed and lay your legs flat.
1) Massage the thigh. Place your hands on the lower end of the thigh and then press them with increasing pressure towards the affected knee. Repeat these steps for three minutes.
2) Press the knee with your palms and follow these steps:
• Press with both hands simultaneously the left and right side of the affected knee. (1 minute)
• Two hands simultaneously press the top and bottom of the affected knee. (1 minute)
• Press and rub the knee until the knee feels warm. (About 2 minutes)
3) Press the acupuncture point
Using your fingertip press the "Middle of the Crook" (Bladder 40) acupuncture point (Chinese "Wei Zhong”) between the two ligaments behind the knee. Apply strong pressure.
4. Rehabilitation therapy
In the early stages, you can rest in bed and lift the affected limbs with an elastic bandage. During the treatment phase, the training of the quadriceps muscles can improve the muscle’s relaxation and contraction. In the later period, knee-flexion exercises can eliminate articular effusion, prevent quadriceps muscle atrophy or recurrent synovitis, and restore the flexion and extension function of the knee joint.
Method: Pull your heel to the hips and stretch the muscles for 15 to 20 seconds.

5. Food therapy
1) Favourable food:
For people with synovitis, high-protein and vitamin-rich foods are suitable. These include eggs, fish, shrimp, beans, potatoes, beef and chicken. Here is a recipe that many interest you:
Ingredients: a chicken, ginger (100g to 250g)
Directions:
• Cut the chicken into small pieces.
• Slice the ginger.
• Fry the chicken and ginger for a few minutes on a high flame and then simmer until cooked.
• When cooking avoid adding oil and salt.
Eating this dish once or twice a week is good for synovial patients who are sensitive to cold.
2) Unfavourable food
• Avoid all dairy products, peanuts, chocolate and millet. These foods can easily cause allergies and trigger a relapse in arthritis or worsen it.
• Reduce the intake of high animal fats (such as lard and suet) and foods high in cholesterol, as the metabolic and inflammatory mediators produced by these foods, can inhibit T-lymphocyte function, which causes and aggravates knee pain, joint swelling, bone decalcification, osteoporosis and joint destruction.
• Eat less sweet foods because sugar can easily cause allergies and worsen synovitis.
• Drink less coffee and tea and avoid active and passive smoking.
• Avoid spicy foods such as pepper and
• foods that easily cause inflammation, such as seafood.
Prevention of synovitis
1. Most importantly, try and prevent injury of the knee. People (such as dancers, athletes and goalkeepers) who perform lower limb sports should pay more attention to the combination of work and rest, and prevent muscle and joint injuries. Otherwise, they are susceptible to bone hyperplasia with advancing age.
2. If a fracture occurs in the knee joint, it is necessary to consult an orthopaedic specialist so that the joint can be reset as soon as possible. If the restoration is not satisfactory, surgical treatment should be timely.
3. To reduce the strain on joints, overweight people should take control of their diet, including adjusting their diet structure, reducing the absorption of heat and keeping the body weight at a healthy level.
4. Seniors should take some medications that contain calcium and vitamin D, which is helpful for bone metabolism. In addition, moderate physical activity can slow the ageing of bone tissue and degenerative changes.
Share: