Muscle Pain and Swollen Joints - Fibromyalgia Syndrome
Ask a Question
Do you suddenly experience stiffness and muscle pain even though you did no exercise? These symptoms can also be accompanied with painful joints. In addition, these symptoms may not have disappeared after three months. If that is the case, you may be suffering from ‘fibromyalgia’.
Overview
Fibromyalgia, also known as fibromyalgia syndrome (FS), is a medical condition (not a type of arthritis) characterised by chronic, widespread musculoskeletal pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disorders, and stiffness, most commonly occurring in women. Secondary fibromyalgia syndrome can be caused by types of trauma or rheumatism, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. In some cases, sufferers who have the symptoms of FS without other diseases get primary fibromyalgia syndrome. In Chinese medicine, FS can be traced back to ‘Bi zheng’ (rheumatic diseases) which attack movement, muscles, legs, and hips.
1. Symptoms
1) Main symptoms
Widespread pain and tender points are the most common signs of all the FS sufferers. The sharp pain attacks several areas of the body, such as joints, muscles and skin, and is accompanied by mood swings. FS can affect any fibrous tissue or muscle, especially in the neck, shoulder, chest, ribs, back of the waist and legs.
2) The pain has been present for at least three months, maybe even many years.
3) Other specific symptoms besides the pain are sleep disorders and tiredness, which manifest in insomnia, frequent nocturnal awakenings and nightmares. Fatigue is present in 50% to 90% of patients.
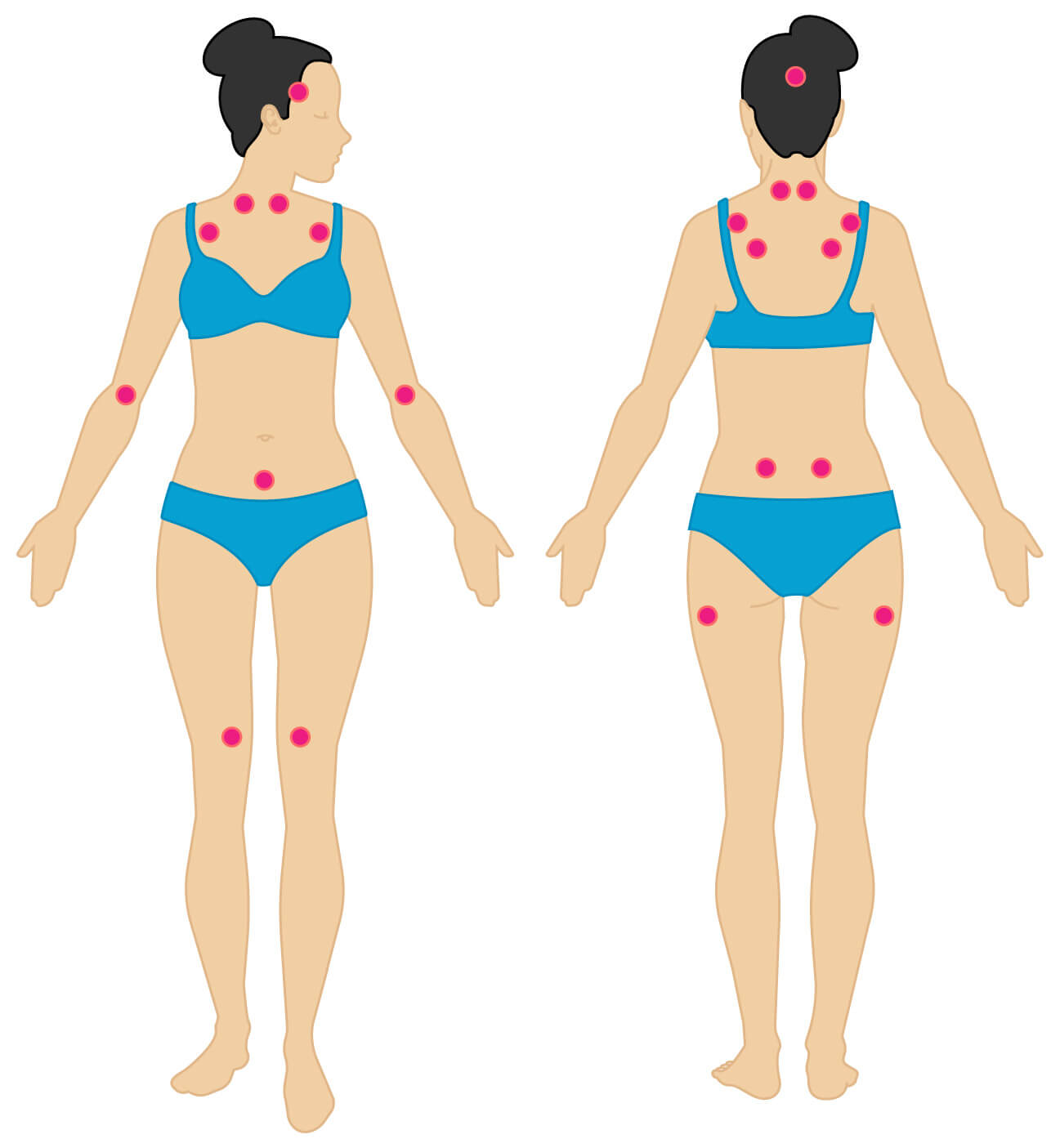
(Fibromyalgia Tender Points)
2. Complications
1) The most common accompanying symptoms include numbness, headache and irritable bowel syndrome.
2) In some cases, depression or anxiety occurs (often aggravated by damp weather, nervousness and overwork)
3) Most FS patients simultaneously suffer from a form of rheumatism such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Other diseases: hypothyroidism, malignant tumour and trauma
Cause of fibromyalgia
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is still unclear, but it most likely involves a variety of factors related to:
1) Sleep disorder. Nervousness and noise can affect sleep quality and lead to worsening of fibromyalgia.
2) Abnormality of neurotransmitters secretion: Some research has shown that the onset of fibromyalgia can be linked to the abnormal secretion of neurotransmitters.
3) Immune disorder. In people with fibromyalgia, the endothelial cell of the blood capillary swells in the muscle caused by dysfunction of immunity, indicating the risk of acute vascular damage, tissue oxygen deficiency, and increased permeability. Some unexplained symptoms of weight gain, swollen hands and frequent urinary at night can be triggered by high cell permeability.
4) Infection. Some illnesses appear to trigger or exacerbate fibromyalgia, such as EB virus and spirochete infection.
5) From the perspective of Chinese medicine, fibromyalgia is associated with unfavourable factors such as wind, cold and dampness. For example, sleeping on a damp floor or experiencing cold wind can give rise to ischemic spasms in muscles, resulting in the production of a large number of harmful metabolites that can stimulate the receptor and cause a painful sensation.
Treatment of fibromyalgia
There is no specific cure for fibromyalgia, but a variety of medications and non-medical treatments may help to improve sleep, reduce the susceptibility to pain receptors, and increase muscle blood flow.
1. General treatment
To eliminate the triggers that can aggravate fibromyalgia, you should strictly limit or eliminate the following risk factors:
• Cold and damp environments
• Physical and mental fatigue
• Excessive or insufficient physical activity
• Nervousness and anxiety
2. Medical treatment
Medications help to minimise the symptoms of fibromyalgia such as reducing pain and improving sleep. Common choices are:
• Amitriptyline, an antidepressants, is often prescribed by doctors. It can relieve pain, insomnia and morning stiffness. However, as amitriptyline causes side effects such as sore throat, constipation and blurry vision, it should not be prescribed to people with severe heart disease and glaucoma.
• Cyclobenzaprine helps to ease the pain and insomnia associated with fibromyalgia.
• Chlorpromazine, taken before sleep, helps to improve sleep and reduces pain and tenderness in the muscles.
3. Psychotherapy and physical therapy
Fibromyalgia tends to attack young women who suffer from obvious neuropsychiatric symptoms like headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. They should accept psychotherapy to get proper guidance.
Appropriate sports can improve strength, stamina, and flexibility.
4. Dietary therapy
1) Suitable foods should contain:
• Many calories
• High in protein and vitamins
• Calcium and phosphorus
For example:
• Carrots are rich in vitamins and mineral salts.
• Cabbage contains Beta-carotene, iron and magnesium, which helps to absorb calcium. In addition, the potassium in cabbage can remove the salt from the body by increased urination.
• Cauliflower is full of vitamin C.
2) Inappropriate foods and drinks refer to
• Spicy, fatty, and fried foods, such as pepper and soybeans
• Food high in iodine, like kelp.
• Tobacco and stimulating drinks like coffee, tea, and caffeine-containing beverages.
3) Tips that help with fibromyalgia
• People with fibromyalgia should limit the intake of milk and food like peanuts, chocolate, millet, cheese and lactose as these foods can cause allergies and aggravate existing arthritis.
• Fatty meats, high saturated fat foods, and high cholesterol foods should be avoided because they can produce metabolites and inflammatory mediators that inhibit the operation of T lymphocytes, which can trigger or worsen pain, swelling and osteoporosis in joints, as well as destroying or worsening joints.
• Desserts are prone to triggering allergies and exacerbate the inflammation of the synovial joints, leading to sore and painful joints.
• To prevent the exacerbation of arthritis, you should limit the intake of wine, coffee, tea, and other beverages and avoid second-hand smoke.
• It is advisable to eat more eggs, fish, shrimps, pulses, potatoes, beef (especially the ‘tendon’) and chicken. These foods contain histidine and collagen that can protect the joints.
Prevention of fibromyalgia
The exact events that trigger the onset of fibromyalgia are unknown, so there is no known way to prevent it. Staying healthy, however, can prevent a number of illnesses.
1. To reduce, eliminate or avoid the risk of suffering from fibromyalgia, you should improve the environment in which you live, create a healthy lifestyle, prevent infections, implement nutritional hygiene, follow a sensible diet and avoid cold and damp environments.
2. Through appropriate exercises, the physical immunity is improved. In addition, overwork, excessive exercise, drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking can damage your health. Try to maintain mental balance and overcome anxiety and nervousness.
3. If you find your symptoms are related to fibromyalgia, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Building trust and insisting on treatment will help you to overcome the disease with courage.
Share: