Foot or Ankle Pain with Swollen Joints—Rheumatoid Arthritis
Ask a Question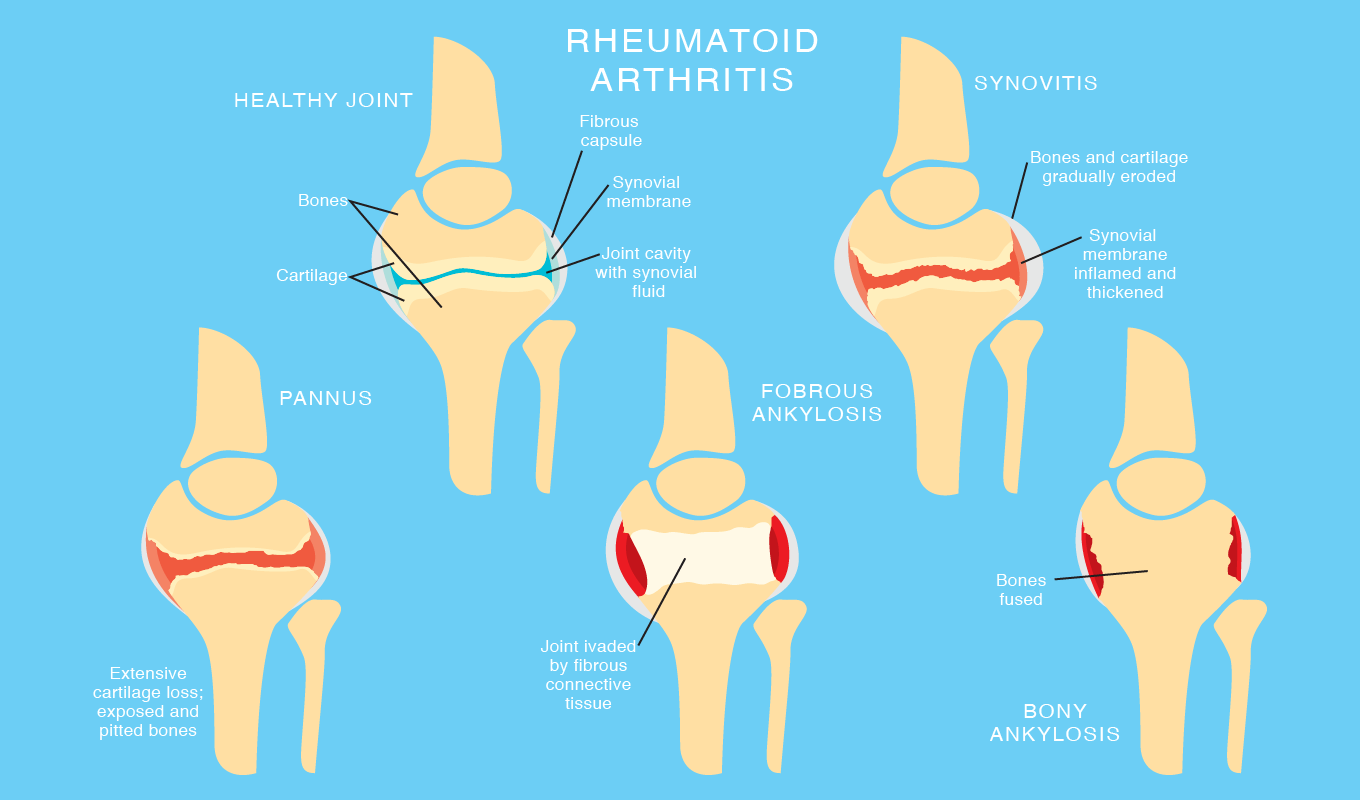
Have you ever had sudden pain and stiffness in the joint of the foot or ankle, sometimes in the shoulder and wrist? Although you did not do excessive exercise the day before? You may google the symptoms, but there is no exact illness you can define because they correspond to various illnesses. Maybe this article can help you to solve the confusion.
Overview
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), is a chronic and systematic inflammatory disorder that affects the joints and belongs in the category of autoimmune diseases. It occurs again and again in the joints of the hands and feet, accompanied by the symptoms of redness, heat and swelling. In the advanced stage, the joints become stiff and deformed, accompanied by skeletal muscle and skeletal atrophy. The inflammation always attacks the lining of the joints and then impacts the tissues of the heart, lungs and eyes and leads to chronic, symmetrical and multiple injuries not only in the joints but throughout the body.
1. Symptoms
• Stiffness of the joints, especially in the morning, after which the pain occurs. This discomfort may decrease or disappear at lunchtime or after doing an appropriate activity.
• Inflamed joints appear symmetrical in metacarpal bones, wrist, shoulder, fingers, ankles and knees, accompanied by redness, swelling, heat, pain and impaired physical activity.
• Deformity. In the final stage, the metacarpal joint is deformed and the foot looks like a claw.
2. Complications
The injury to the joints can lead to physical disability, but not death. In fact, it is the complications that lead to death, so people should attach importance to the prevention or treatment of complications. Here are some of them:
• Rheumatoid nodules
• Rheumatoid vasculitis
• Rheumatoid heart disease
• Rheumatoid lung disease
• Kidney damage
• Eye disease
• Sjogren syndrome (an autoimmune disease)
• Digestive disorders
3. Difference to similar diseases
• Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a non-inflammatory disease occurring in people over forty with no systemic illness or swollen joints and mainly affects the joints of the knee and spine.
• Rheumatism
Rheumatism, caused by streptococcal infection, has the characteristics of:
• Acute onset of symptoms of sore throat, fever and increasing white blood cells.
• The lesion occurs in the limbs and leaves no damage after recovery.
• Heart inflammation occurs simultaneously.
Cause of Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no exact cause of RA, but it is believed that hereditary factors and environmental triggers are relevant. The articular tissue, which is attacked by the autoimmune system, leads to inflammation and swelling of the joints, which interferes with the normal function of bone and cartilage.
According to western medicine, rheumatoid arthritis can be triggered by the environment, bacteria, viruses, genes and hormones.
1. Bacterial factor: It was found that Streptococcus bacteria are able to sustainably stimulate an antigen that can exist in the body for a long time. In this process excessive immunity will damage the joints to some extent, leading to rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Viral factor. Some cases indicate that RA patients always have viral infections such as EBV (Epstein-Barr virus) at the same time.
3. Genetic factor. The risk of RA in families is higher than in individuals. It may relate to leukocyte antigen.
4. Hormone factor. Some research shows that RA occurs much more often in women than in men. However, the symptoms may decrease during pregnancy or after taking the contraceptive pill.
5.Environmental factors. These include cold or damp environments, fatigue, malnutrition, trauma and spiritual changes.
According to Chinese medicine, rheumatoid arthritis can be attributed to liver and kidney deficiencies and pathogenic evils such as coldness and dampness. Congenital physical defects and inappropriate diet or lifestyle can damage the functions of the liver and kidneys. In TCM theory, the liver controls the muscle function and kidneys influence the movement of the bone. Once the pathogens attack the muscles and bones, people are prone to get rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis should focus on maintaining flexibility and joint coordination. However, there is no specific treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, and the methods at the various stages are different.
1. General therapy
During the acute phase, sufferers who have swollen joints should lie down until the symptoms subside. However, to avoid joint stiffness and shrinkage of muscles, sufferers should exercise more to relieve the joints and accept physiotherapy. In addition, a healthy diet rich in protein and vitamins is necessary.
2.Western Drug therapy
There are two types of medication that are commonly used to treat rheumatoid arthritis; one is a non-specific drug that aims to relieve the inflammation; another is an anti-inflammatory drug, which can quickly dissolve the illness.
1) Non-specific drugs
• Anti-inflammatory drug or painkiller: This medication relieves pain and inflammation by inhibiting the release of prostaglandin. The long-term intake, however, can not change the situation of RA but increases the side effects.
• Glucocorticoid has obvious efficacy in controlling the symptoms of RA, but it also fails to deal with the root of the problem. In some cases, glucocorticoid is not the primary choice and should be controlled for prolonged use due to complications and multiple side effects.
2) Anti-rheumatic drugs
“Gold salt” is the common medication used for the rapid treatment of RA. It does not cure RA, but helps to control the disease by relieving joint pain and stiffness in the morning. Users always experience side effects like rash, dermatitis, stomatitis, proteinuria (excessive amounts of protein in the urine), bloody urine, and the loss of leukocytes (white blood cells) and blood platelets.
3) Biological agent
This drug aims to improve cellular immunity and adjust the immune dysfunction by combining it with other anti-inflammatory drugs. However, the sole use of immunomodulators has no explicit effectiveness.
3. Surgery
If the drug therapy is not effective, you should accept surgery to repair damaged joints and restore the ability to use the joint. In the later stage of rheumatoid arthritis, joint excision or joint fusion, especially in the foot, can help alleviate the pain and allow more flexible walking.
4. Diet therapy
1) Suitable food. People with rheumatoid arthritis should eat foods containing the following
• Rich multiple foods, such as lean meats, fish and milk.
• High in vitamins like vegetables and fruits.
For instance,
• Lean meat. In addition to vitamin C and E, lean meat contains many different proteins that can easily be digested by the body, which increases physical performance. In addition, phospholipids of meat are beneficial for the growth and development.
• Millet. You can cook millet porridge because it has a variety of vitamins, amino acids, fat, fibre and carbohydrates. For example, carotene may be found in millet but not in other foods. Of all the vitamins in millet, vitamin B is the major component.
• Fruit. Apples are recommended for people with RA because it contains several vitamins, minerals, sugar and fat. You can eat an apple between two meals every day.
2) Unsuitable food
Guiding principles
• During the acute phase of rheumatoid arthritis - when the ankle swells - you should limit eating spicy food.
• If you have a weak spleen and stomach, avoid eating cold food, shrimps and crabs.
For example,
• Pepper is unsuitable for the person suffering from acute arthritis until the situation stabilises.
• Pears can interfere with the digestive function of the stomach and spleen, so people who have a stomach disorder should not eat pears.
3) Recommended recipes
Pork & Pepper root soup
Method:
• Clean the lean pork and pepper root
• Put the pepper root in a clean gauze bag
• Put the meat and bag into the water
• Bring to the boil over high heat, then simmer on low heat for 30 minutes
• Drink the soup and eat the meat
• This soup helps to nourish the stomach and remove moisture to relieve the severe pain in the joints.
5. Massage therapy (on lower limbs)
• Lie in prone position. Your therapist will knead the muscles from the back of the buttocks to legs and tendons and then return to your buttocks. Repeat this process two to three times.
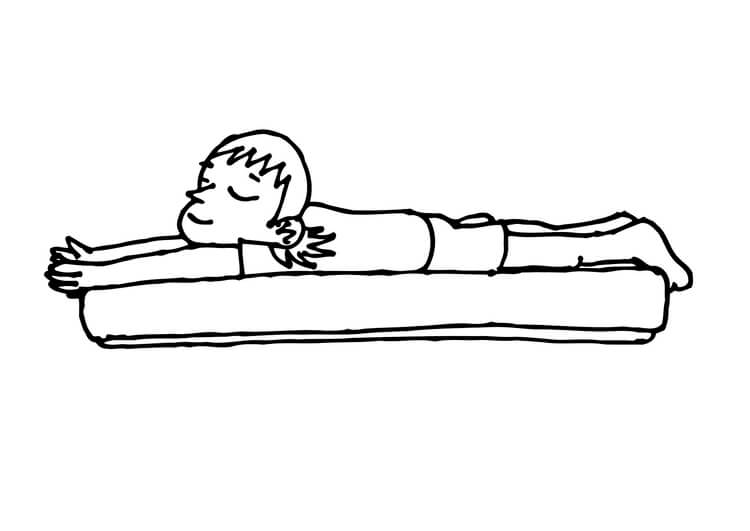
(Prone Position)
• Lie flat on the bed. Your therapist will knead your lower limbs in the sequence of the front and two sides of your thigh, then the outside of your calf, instep, and toe joint. Flexion of the ankle should cooperate at the same time.
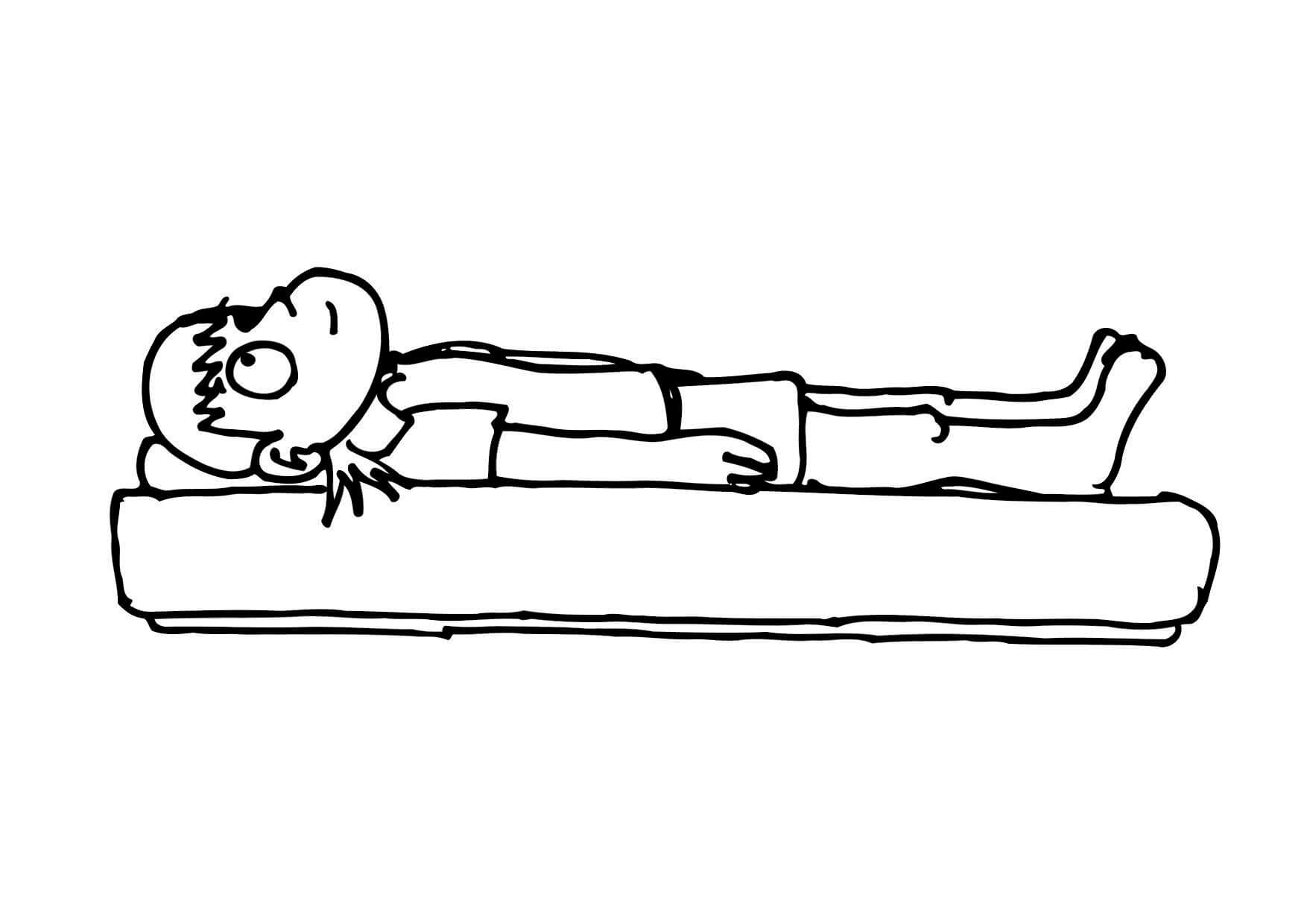
(Lie flat)
Prevention of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Because the cause is unknown, there is no specific prevention of rheumatoid arthritis. According to clinical experience, physicians around the world have come to the conclusion that people can prevent RA by moving away from the risk factors of RA and keep a healthy lifestyle and diet. Try to:
1. Enhance exercise and strengthen physical health
Take part in regular physical exercises such as health gymnastics, qigong, Tai Chi, sports gymnastics and walking. People who are physically active are stronger than those who are not physically trained because the former have a strong ability to resist the invasion of cold and dampness.
2. Avoid the attack of wind, cold and dampness
Before the onset of RA, most patients had experienced cold and damp attacks that play an important role in the occurrence and development of this disease. For example, in spring you are very vulnerable to RA, which means you should avoid cold environments, dampness and rain during this season. To keep the joints warm, you should not wear wet clothes, wet shoes and socks, as TCM states that damp clothing can attack the joints. In summer avoid air conditioners blowing straight at you, even though you feel hot. And excessive drinking of cold water or beverages is harmful to you. Moreover, keeping warm is the most important thing to prevent invasion by the cold.
3. Keep a balance between work and leisure
To combine work and rest, activities and rest should be moderate. Overload can reduce immunity and lead to some diseases.
4. Keep a happy mind
The onset and development of the disease are closely related to the state of mental activity. Maintaining a happy mind is also key to preventing rheumatoid arthritis. Overstimulation or long-term mood swings can affect one’s health to some extent. We must learn to control negative emotions, study hard and work actively with a positive attitude. Maintaining a healthy mind is important to maintain normal immune function in the body.
5. Prevent and control infection
Experimental studies have shown that bacterial or viral infections may be one of the causes of rheumatoid arthritis. Some RA cases are caused by infectious diseases such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, chronic cholecystitis and dental caries. Therefore, preventing or controlling infections is crucial for the protection against rheumatoid arthritis.
Share: